NO.241 HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription.
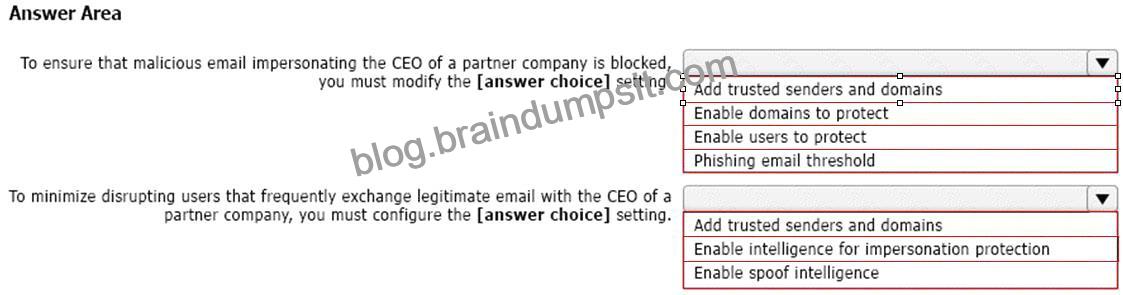
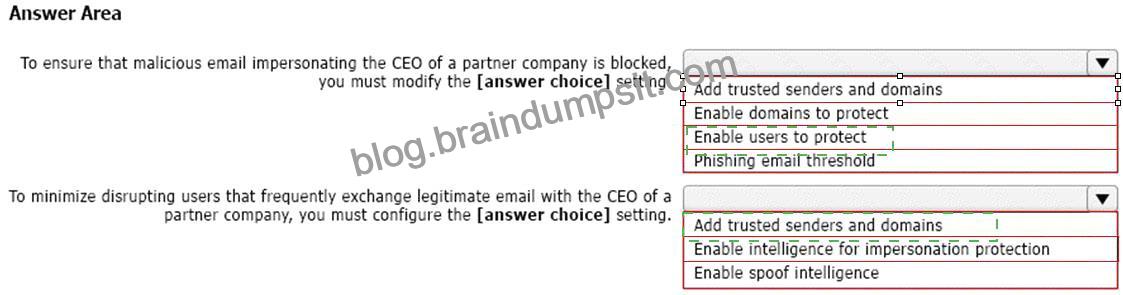
You deploy the anti-phishing policy shown in the following exhibit.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation
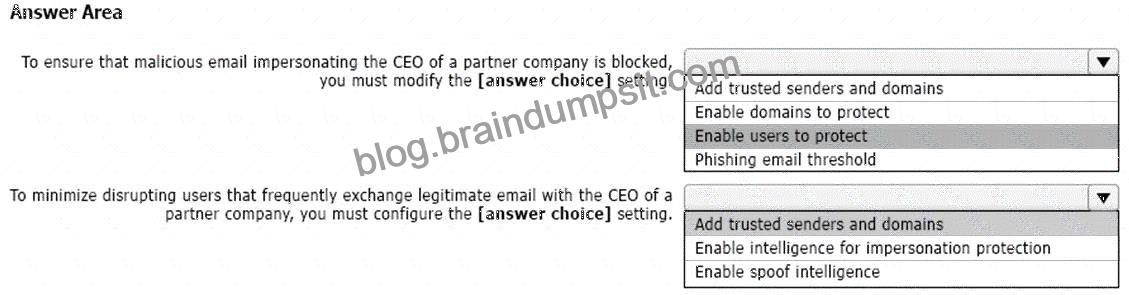
Box 1: Enable users to protect
Anti-phishing policies in Defender for Office 365 also have impersonation settings where you can specify individual sender email addresses or sender domains that will receive impersonation protection.
User impersonation protection
User impersonation protection prevents specific internal or external email addresses from being impersonated as message senders. For example, you receive an email message from the Vice President of your company asking you to send her some internal company information. Would you do it? Many people would send the reply without thinking.
You can use protected users to add internal and external sender email addresses to protect from impersonation.
This list of senders that are protected from user impersonation is different from the list of recipients that the policy applies to (all recipients for the default policy; specific recipients as configured in the Users, groups, and domains setting in the Common policy settings section).
When you add internal or external email addresses to the Users to protect list, messages from those senders are subject to impersonation protection checks. The message is checked for impersonation if the message is sent to a recipient that the policy applies to (all recipients for the default policy; Users, groups, and domains recipients in custom policies). If impersonation is detected in the sender’s email address, the action for impersonated users is applied to the message.
Box 2: Add trusted senders and domains
Trusted senders and domains
Trusted senders and domain are exceptions to the impersonation protection settings. Messages from the specified senders and sender domains are never classified as impersonation-based attacks by the policy. In other words, the action for protected senders, protected domains, or mailbox intelligence protection aren’t applied to these trusted senders or sender domains. The maximum limit for these lists is 1024 entries.
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/office-365-security/anti-phishing-policies-about